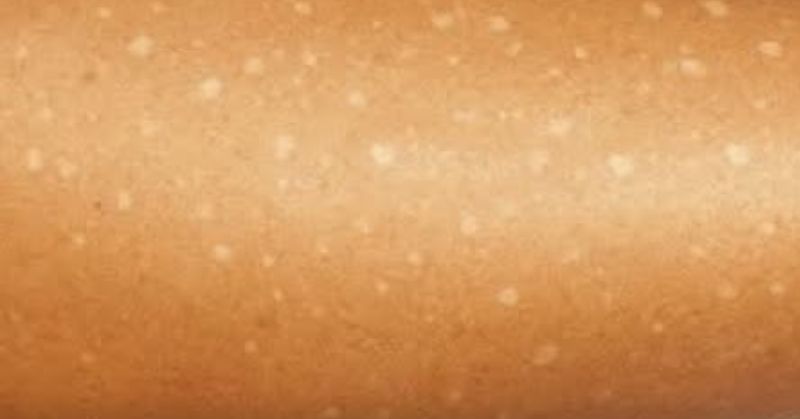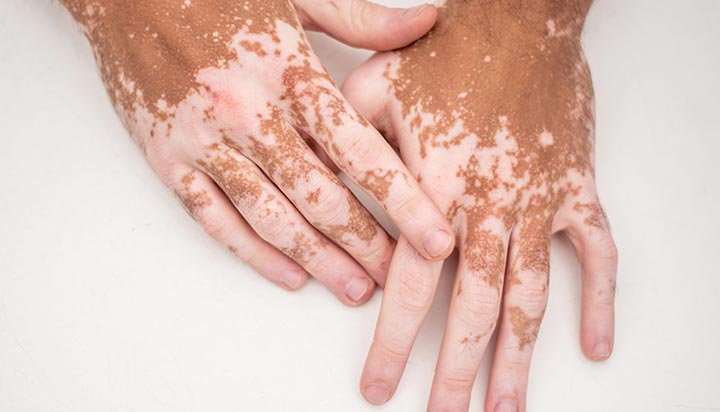
Vitamin B12 Deficiency
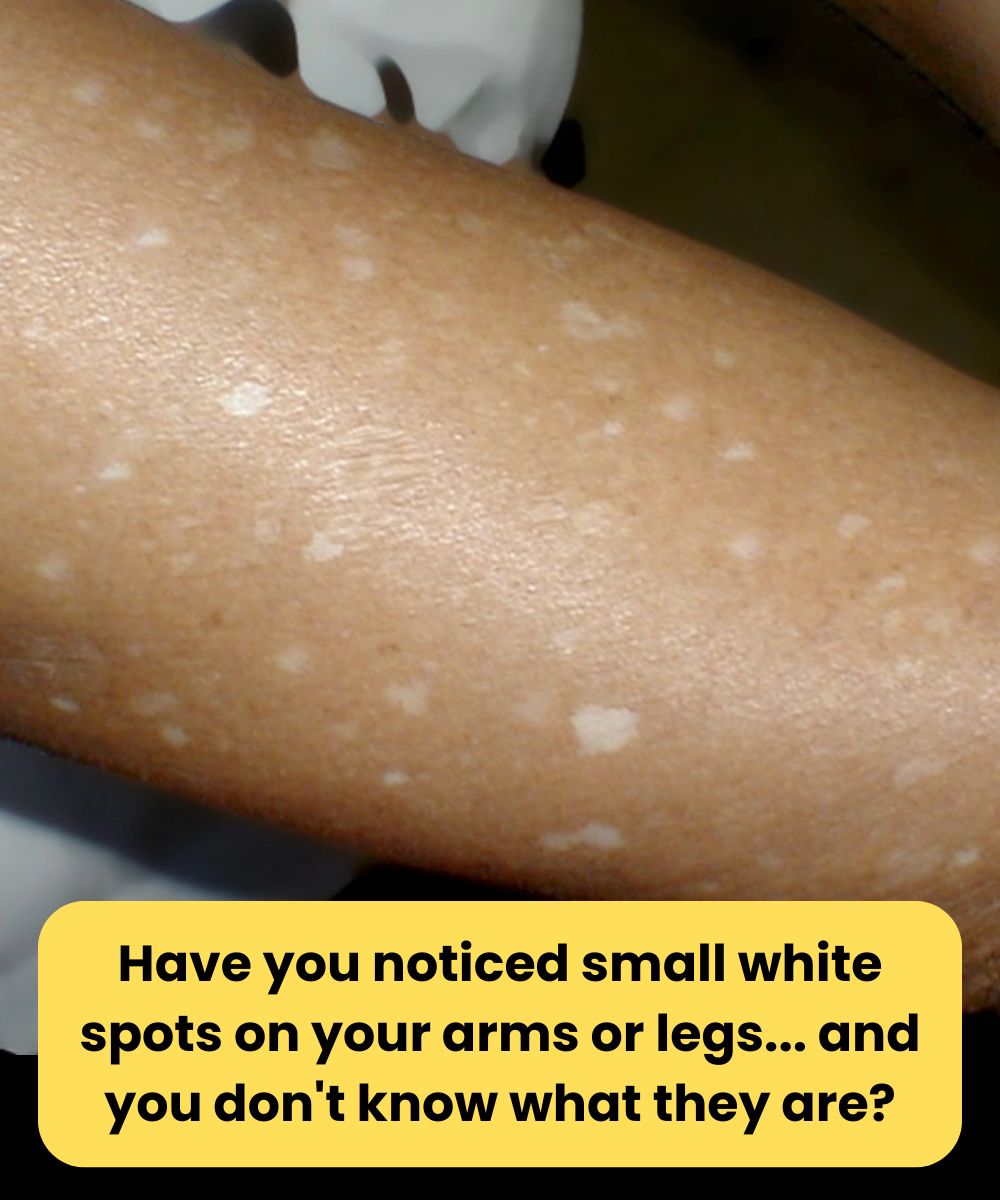
One of the most common vitamin deficiencies linked to white spots on the skin is vitamin B12 deficiency. This vitamin plays a vital role in red blood cell formation, nerve function, and DNA synthesis. A lack of B12 can lead to a condition called vitiligo, where the skin loses its pigment, resulting in small or large white patches.
Vitamin D Deficiency
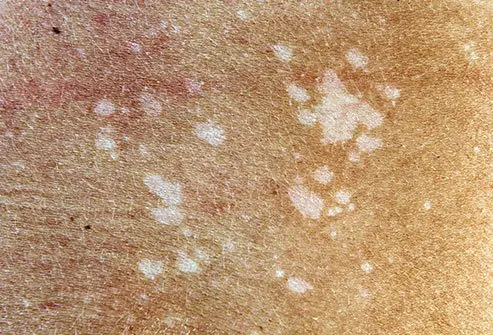
Vitamin D is another essential nutrient for skin health. It is primarily synthesized in the skin through sunlight exposure and is vital for immune function and skin cell growth. A deficiency in vitamin D may contribute to skin issues, including the development of white spots or uneven pigmentation.
Calcium and Other Minerals
Calcium works closely with vitamin D to maintain healthy bones, but it also affects the skin. Low calcium levels can sometimes lead to changes in skin pigmentation, including white spots, although this is less common. Similarly, deficiencies in zinc and copper can affect skin pigmentation because these minerals are involved in melanin production, the pigment responsible for skin color. A balanced diet rich in leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and whole grains can help maintain adequate mineral levels.
Other Factors to Consider
Therefore, persistent or spreading white spots should always be evaluated by a healthcare professional or dermatologist to rule out other underlying causes.
How to Support Healthy Skin
To prevent white spots caused by nutrient deficiencies, focus on a balanced diet that includes:
- Leafy green vegetables (spinach, kale) for B12 and minerals
- Dairy products or fortified alternatives for calcium and vitamin D
- Eggs, fish, and lean meats for B12 and zinc
- Sunlight exposure in moderation to naturally boost vitamin D
Additionally, supplements may be recommended by a doctor if dietary intake is insufficient. Regular skin check-ups and awareness of early changes in pigmentation can help detect problems early and maintain healthy, even-toned skin.

