The primary cause of eye floaters is age-related changes in the vitreous humor—the jelly-like substance that fills the inside of your eyes. As you age, the vitreous can liquefy and shrink, causing microscopic collagen fibers within it to clump together. These clumps cast tiny shadows on your retina, which you perceive as floaters/
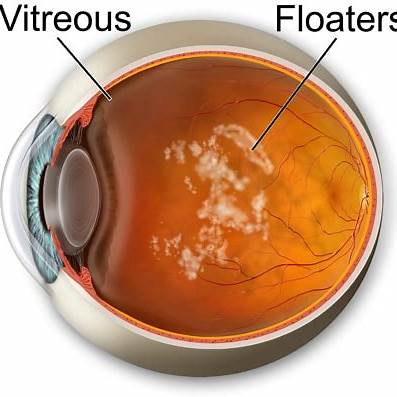
Other causes of eye floaters include:
- Posterior Vitreous Detachment (PVD): A condition where the vitreous pulls away from the retina, common in individuals over 50.
- Retinal Tears or Detachment: Serious conditions where the retina peels away from its underlying layer, requiring immediate medical attention.
- Inflammation in the Eye (Uveitis): Can cause the release of inflammatory debris into the vitreous, leading to floaters.
- Hemorrhaging: Bleeding into the vitreous due to injury, diabetic retinopathy, or hypertension.
- Eye Surgeries and Medications: Certain procedures and drugs can increase the likelihood of developing floaters.
When to Seek Medical Attention
- A sudden increase in the number of floaters
- Flashes of light in the same eye as the floaters
- Loss of peripheral vision or a shadow over your vision
- Eye pain or discomfort
These symptoms could indicate serious conditions like retinal detachment, which can lead to permanent vision loss if not treated promptly.
Diagnosis of Eye Floaters
Continue reading…
